There is a lot of discussion about brake pads, but most of it focuses on the friction materials they use. In fact, there is also a lot worth discussing in depth about the bike disc brake pad backing plates used in brake pads.
1. Bike Disc Brake Pad Backing Plates Materials
The bike disc brake pad backing plates usually use the following materials:
1.1 Steel (iron-carbon alloy with a carbon content between 0.02% and 2.11%)
Steel has high strength and hardness. It can withstand large braking forces and is not easy to deform. At the same time, steel has good thermal conductivity. It helps to dissipate heat quickly during braking to prevent the brake pads from reducing braking performance due to overheating. Most importantly, the cost of steel disc brake pad backing plates is relatively low. Usually, the price of brake pads made of steel is not very high.


1.2 Aluminum alloy
Aluminum alloy is an alloy formed by adding other elements (such as copper, silicon, magnesium, zinc, etc.) to aluminum as the base. It has the advantages of low density, high specific strength, good corrosion resistance, and easy processing. It helps to reduce the overall weight of the bicycle and improve riding performance. At the same time, aluminum alloy has good thermal conductivity. It can quickly dissipate the heat generated during braking, reduce the temperature of the brake pads, and improve the stability of braking performance. However, the strength of aluminum alloy is relatively lower than that of steel. When the brake pad bears a large-intensity braking force, it may deform to a certain extent.
1.3 Carbon fiber
This is a familiar high-tensile strength material made of carbon fiber cloth and resin. Carbon fiber materials have an extremely high strength-to-weight ratio. They are both lightweight and strong, which can maximize the weight reduction of the bicycle while ensuring braking performance. They are particularly suitable for high-end bicycles that pursue extreme lightweight. Carbon fiber also has good fatigue resistance. It can withstand frequent braking impacts. In addition, the carbon fiber material has a beautiful appearance and a unique texture, which can enhance the overall texture of the bicycle. However, obviously, the cost of carbon fiber disc brake pad backing plates is high and the price is expensive. Moreover, when subjected to external impact, they are prone to cracks or damage, and the maintenance cost is also unacceptable to many people.
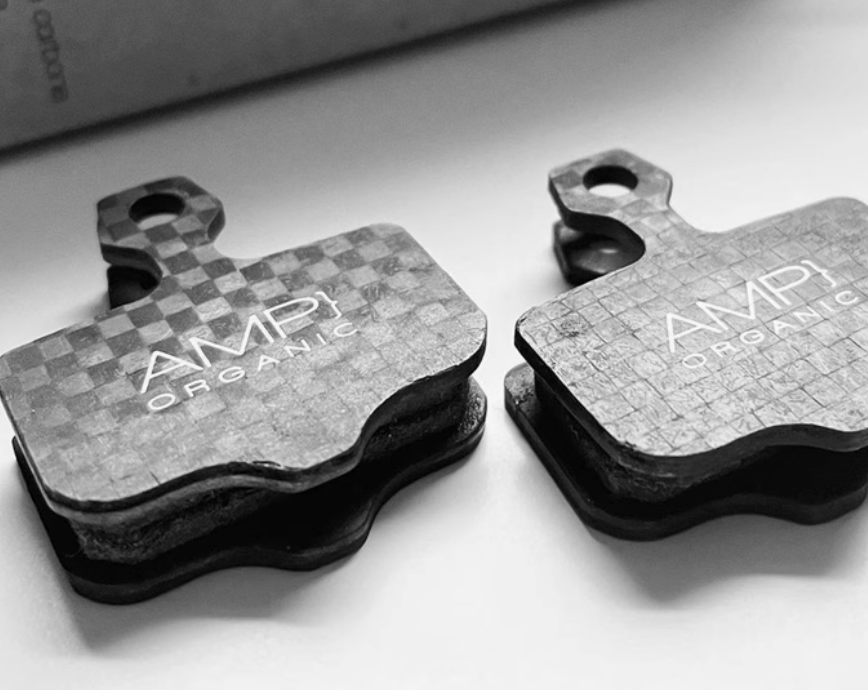
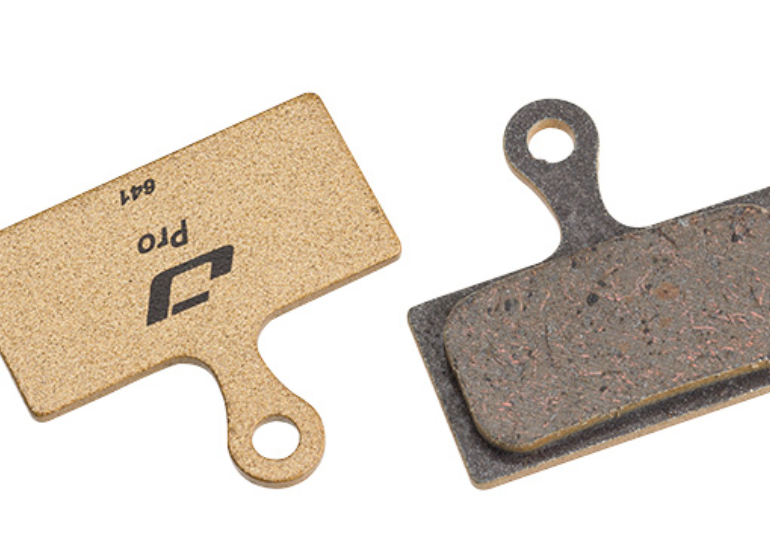


1.4 Composite materials
Composite materials are usually made by combining multiple materials. Composite materials combine the advantages of various components. They have both a certain degree of strength and rigidity and can reduce weight. The molding process of composite materials is relatively flexible. They can be made into disc brake pad backing plates of various shapes and structures according to different design requirements to optimize braking performance and heat dissipation effects. At the same time, composite materials also have good insulation performance. They can effectively prevent static electricity and electromagnetic interference. However, the performance of composite materials may be affected by environmental factors. For example, in high-temperature or humid environments, their performance may decline. At present, not many brake pads use composite materials as backing plate materials.
2. Disc Brake Pad Backing Plates Shape
2.1 Why are there so many different shapes and styles?
The shape and style of bicycle disc brake pads are designed by brand manufacturers of disc brake calipers such as SHIMANO and SRAM. Each brand has only a limited number of caliper models and corresponding disc pad styles. That is to say, if you look for brake pads in the product line of the caliper brand, you can easily find the new brake pads you need. However, with the emergence and gradual growth of third-party brake pad manufacturers, in many cases, the brake pads produced by third-party manufacturers are more affordable at the same quality. We rarely purchase original brake pads as replacement parts.
Then a problem arises. Third-party brake pad manufacturers will copy the corresponding brake pad products for the shapes and styles of disc brake pad backing plates used by all caliper brands. At the same time, brake pad manufacturers will make new modifications on the basis of the original design to increase the heat dissipation and anti-jitter performance of the original products. This has led to the emergence of many brake pads in the market that have never appeared in the original factory, are not universal, and have no names in the originally unnamed brake pad market. These brake pads that are different in style from the original factory and have no names have made the market more chaotic. When you get a new brake pad, it is difficult for you to be 100% sure whether it can be used on your disc brake caliper.
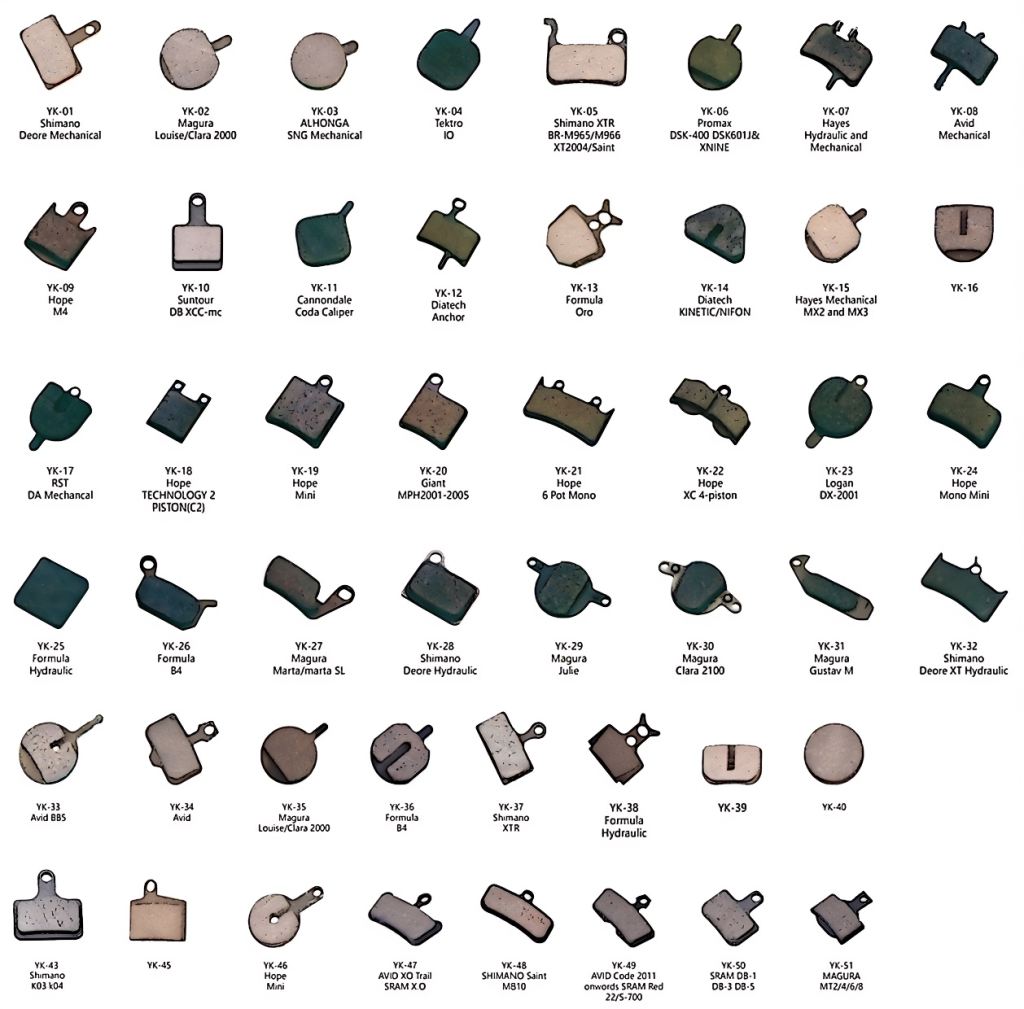
2.2 How to chose the right disc brake pad backing plates shapes
The bad news is that these different shapes do not seem to have corresponding model names one by one. That is to say, when you want to buy new bike disc brake pads, you can only go to bicycle stores or online stores to search for brake pads with shapes similar or identical to those of your old disc brake pad back plates. It seems impossible for you to accurately locate a brake pad of a certain shape by a model name.
The good news is whether a new disc brake pad can be successfully installed in your caliper also depends on whether the backing plate of the new disc brake pad can be successfully placed in the right position. You can always easily find disc brake pads with the same shape as your old brake pads, and basically, as long as the size and model are similar, it should work.
3. Disc Brake Pad Backing Plates Heat Dissipation Design
3.1 Shape design
3.1.1 Heat dissipation fin design
Some disc brake pad backing plates have heat dissipation fins. This design increases the contact area between the brake pads and the air, so that heat can be more quickly dissipated into the surrounding air. There are some cases of brake pads with excellent heat dissipation fin design in the market. For example, LEBYCYCLE’s 02RS resin brake pads are compatible with most Shimano disc brake calipers. Shimano also uses aluminum heat dissipation fins on some high-end brake pads. Aluminum has good thermal conductivity and can quickly conduct heat from the friction material to the fins, and then dissipate heat through air convection.
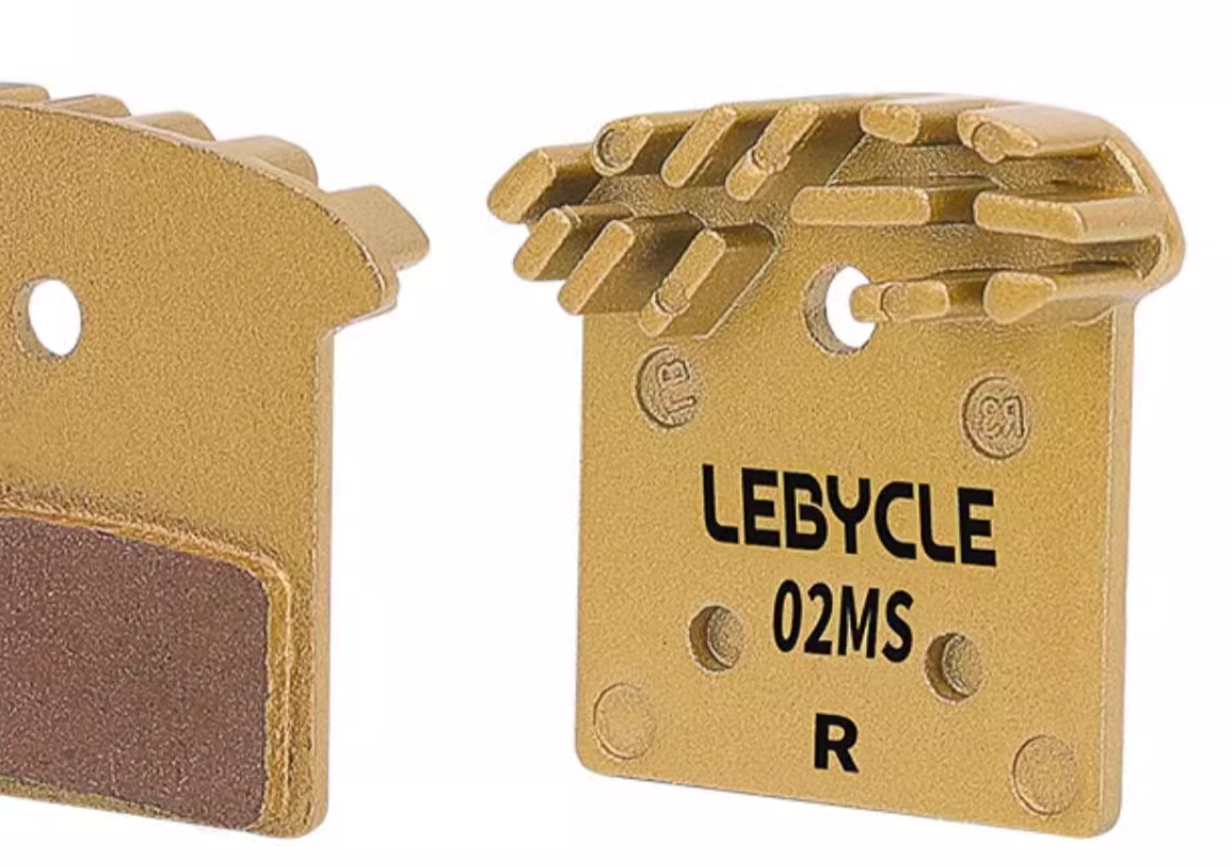


3.1.2 Hollowing out
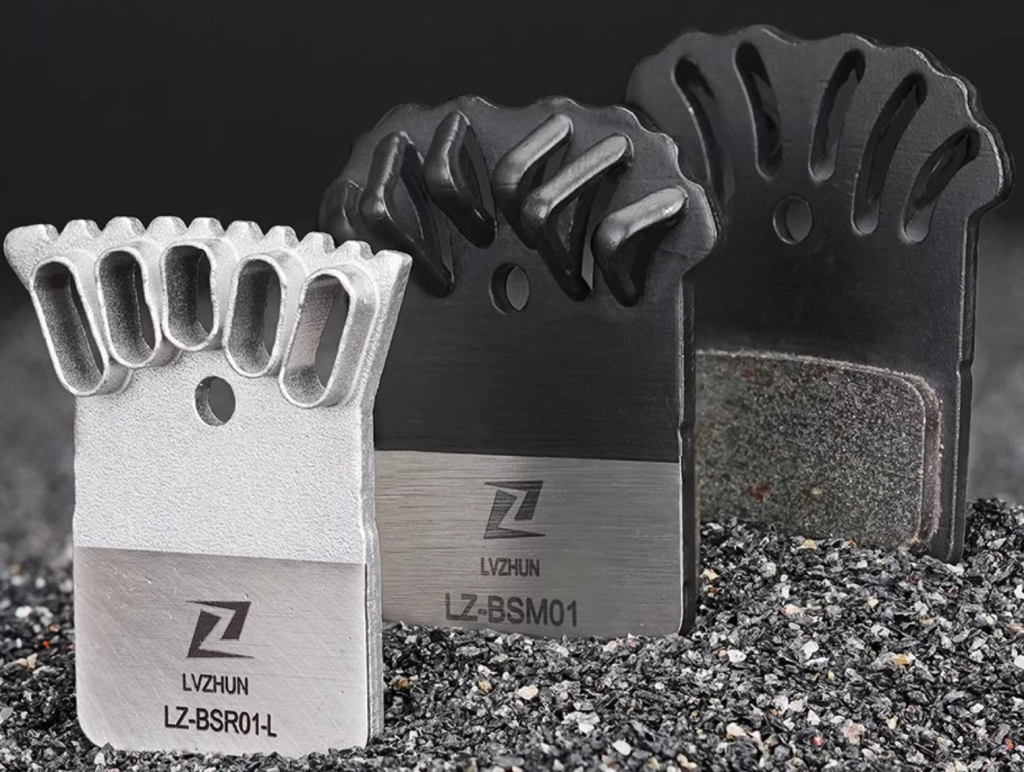
Some high-end brake pads use a hollow design. The flow of air can continuously take away the heat on the surface of the disc brake pad backing plates. Moreover, the hollow design changes the air flow path, making the air form more complex convection around the brake pads, further enhancing the heat dissipation effect. At the same time, it creates more edges and surfaces. These new surfaces increase the contact area with the air, so that heat can be more quickly transferred from the friction material to the air through the backing plate. Just like a heat sink, more surface area means more heat can be dissipated, thereby improving heat dissipation efficiency.
For example, the EggRoll brake pads equipped with the new road hydraulic disc brake kit of L-TWOO have a heat dissipation backing plate designed based on the Venturi effect, which can form a vortex in the back hole during riding to increase the circulation speed of air on the backing plate of the brake pad, thereby taking away more heat.

3.2 Disc Brake Pad Backing Plates Material optimization
3.2.1 Main Material
Some backing plates will choose materials with good thermal conductivity. The French AMP carbon fiber brake pads adopt carbon fiber backing plate technology. They use the shock-absorbing performance of carbon fiber to greatly reduce the resonance generated by the brake pads and caliper pistons during braking, thereby reducing abnormal noise. At the same time, the carbon fiber backing plate can withstand high temperatures and has good heat insulation function. It can resist the heat transfer from the disc to the piston cylinder, thereby greatly reducing the heat accumulation of the caliper and effectively preventing the hand feel linear change caused by the thermal expansion and contraction of the brake fluid in the piston cylinder. In addition, the carbon fiber material can also reduce the weight of the brake pads, which is 25% lighter than the traditional brake pads, helping to improve the overall performance of the bicycle.
3.2.2 Coat
Some v have special heat dissipation coatings. This coating can improve the heat dissipation efficiency of the backing plate and help heat dissipate more quickly from the surface of the backing plate. In terms of thermal radiation capability, the material and surface characteristics of the coating are specially there to enhance the thermal radiation effect. The surface microstructure of some coatings can increase the radiation area, or their chemical composition can have a high emissivity in a specific wavelength range, thereby improving the efficiency of thermal radiation heat dissipation.
For example, AbsoluteBlack Graphenpads brake pads incorporate graphene materials into the backing plate and completely cover them with a graphene heat dissipation coating. Graphene has excellent thermal conductivity and can achieve greater heat conduction from the friction material to the backing plate. It can reduce the temperature of the brake pads and discs by up to 35%, eliminate braking fade, and increase the service life of the brake pads and discs. According to AbsoluteBlack’s tests, a single set of brake pads can last an average of 8,000 kilometers in hilly terrain.
4. How the Backing plate connect to the friction material
4.1 Bonding
Use high-temperature-resistant and high-strength adhesive to bond the friction material with the backing plate. This method provides a tight connection without gaps, helping to reduce noise and vibration. During production, first clean the backing plate to remove surface oil, impurities, etc., to ensure the adhesive can adhere well. Then, apply the adhesive evenly to the contact surfaces of the backing plate and friction material. Finally, cure the adhesive through a certain pressure and temperature to achieve a firm bond between the two.
4.2 Mold casting bonding
This is a special bonding method. It forms an integral whole with the backing plate by injecting uncured friction material into a mold. High temperature and pressure during this process. During specific operation, first apply a layer of special adhesive to the backing plate. Then place the backing plate into the mold. Next, pour the mixed uncured friction material into the mold. Under high temperature and pressure, the friction material gradually cures and forms. It closely connects with the backing plate. This method ensures a tight connection between the friction material and the base plate or bottom plate. It improves braking performance and service life.
4.3 Mechanical connection
Including rivet connection and new mechanical fixed system connection. Rivet connection is a more traditional method. Holes are pre-drilled in the backing plate and the friction material, and then they are fixed together with rivets. However this method weakens the backing plate’s strength due to drilling or punching holes. During braking the backing plate’s bending stress and thermal expansion-contraction easily cause the friction material to crack. The friction material can also separate from the backing plate. Therefore this method is now less popular.
New mechanical fixing systems, such as NRS (Nucap’s patented technology) v, do not have holes. They have some hook structures. During production, place the backing plate and raw friction material into a mold. Under pressure, the friction material is squeezed into the mold. The hooks embed into the friction block to achieve mechanical fixation. This method combines the reliability of mechanical connections and the advantages of the mold casting process. It can effectively improve the performance and stability of brake pads.
By the way, SUMLON has been manufacturing bicycle parts for over 15 years. Contact us if you are looking for a bike parts factory or a one-stop wholesaler. Peace